

Know-All-Edge is an ISO 27001:2013 certified Information Technology services company founded by a team of young and passionate leaders in the technology domain. We offer highly customised solutions & services in the areas of Cyber Security, Infrastructure, Availability, Mobility, Cloud & Hybrid IT. Our solutions are tailor-made to address all your critical business challenges & pain points, enable you to operate more efficiently, and produce more value.
VALUE PROPOSITION
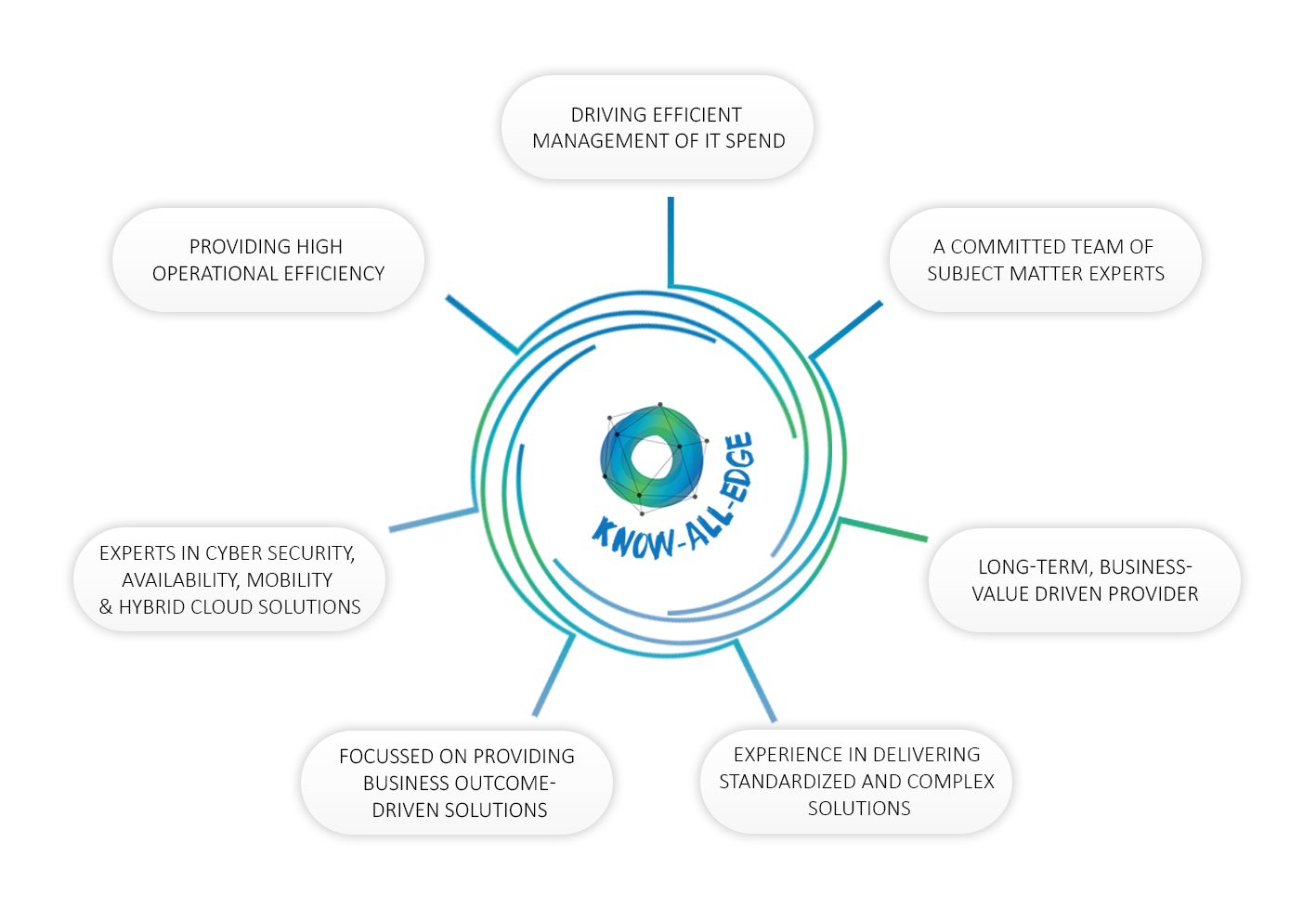
WHY KNOW ALL EDGE?
What our CUSTOMERS has to say?
Testimonial

In Know All Edge, we see a very young and dynamic team, they are very proactive and hands-..
..Read More

In our school, we had several challenges in Network Security, WiFi Infrastructure, and Dat..
..Read More

Working with Know All Edge Team over the past 3 years has been a very positive experience,..
..Read More

Know All Edge has been instrumental in building our IT Operations from scratch, we have wo..
..Read More
Our Clients